Publications

Large Language Models are increasingly used in applications requiring objective assessment, which could be compromised by political bias. Many studies found preferences for left-leaning positions in LLMs, but downstream effects on tasks like fact-checking remain underexplored. In this study, we systematically investigate political bias through exchanging words with euphemisms or dysphemisms in German claims. We construct minimal pairs of factually equivalent claims that differ in political connotation, to assess the consistency of LLMs in classifying them as true or false. We evaluate six LLMs and find that, more than political leaning, the presence of judgmental words significantly influences truthfulness assessment. While a few models show tendencies of political bias, this is not mitigated by explicitly calling for objectivism in prompts. Warning: This paper contains content that may be offensive or upsetting.
Cross-lingual knowledge transfer, especially between high- and low-resource languages, remains challenging in natural language processing (NLP). This study offers insights for improving cross-lingual NLP applications through the combination of parameter-efficient fine-tuning methods. We systematically explore strategies for enhancing cross-lingual transfer through the incorporation of language-specific and task-specific adapters and soft prompts. We present a detailed investigation of various combinations of these methods, exploring their efficiency across 16 languages, focusing on 10 mid- and low-resource languages. We further present to our knowledge the first use of soft prompts for language transfer, a technique we call soft language prompts. Our findings demonstrate that in contrast to claims of previous work, a combination of language and task adapters does not always work best; instead, combining a soft language prompt with a task adapter outperforms most configurations in many cases.
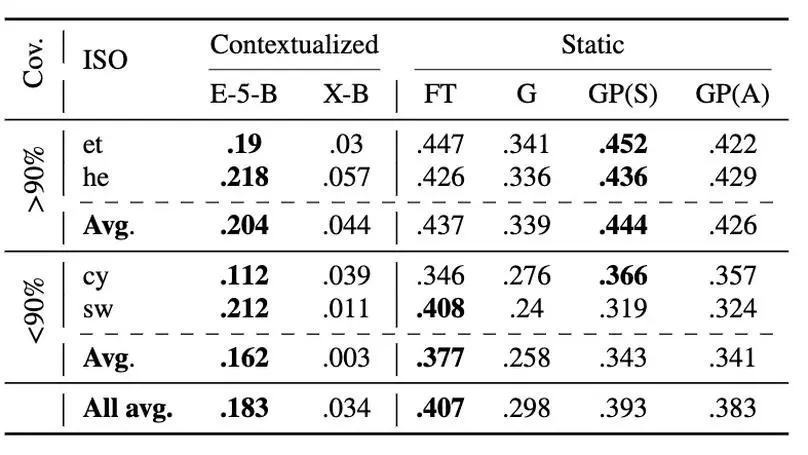
Contextualized embeddings based on large language models (LLMs) are available for various languages, but their coverage is often limited for lower resourced languages. Using LLMs for such languages is often difficult due to a high computational cost; not only during training, but also during inference. Static word embeddings are much more resource-efficient (“green”), and thus still provide value, particularly for very low-resource languages. There is, however, a notable lack of comprehensive repositories with such embeddings for diverse languages. To address this gap, we present GrEmLIn, a centralized repository of green, static baseline embeddings for 87 mid- and low-resource languages. We compute GrEmLIn embeddings with a novel method that enhances GloVe embeddings by integrating multilingual graph knowledge, which makes our static embeddings competitive with LLM representations, while being parameter-free at inference time. Our experiments demonstrate that GrEmLIn embeddings outperform state-of-the-art contextualized embeddings from E5 on the task of lexical similarity. They remain competitive in extrinsic evaluation tasks like sentiment analysis and natural language inference, with average performance gaps of just 5-10% or less compared to state-of-the-art models, given a sufficient vocabulary overlap with the target task, and underperform only on topic classification. Our code and embeddings are publicly available at https://huggingface.co/DFKI.
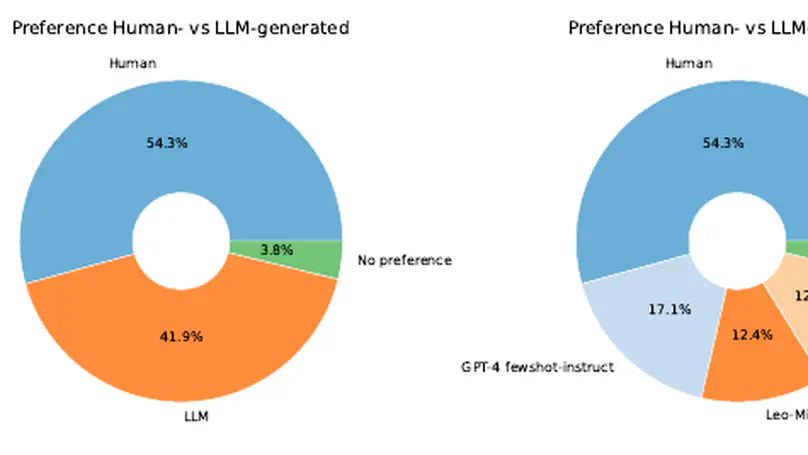
In this paper, we investigate the use of large language models (LLMs) to enhance the editorial process of rewriting customer help pages. We introduce a German-language dataset comprising Frequently Asked Question-Answer pairs, presenting both raw drafts and their revisions by professional editors. On this dataset, we evaluate the performance of four large language models (LLM) through diverse prompts tailored for the rewriting task. We conduct automatic evaluations of content and text quality using ROUGE, BERTScore, and ChatGPT. Furthermore, we let professional editors assess the helpfulness of automatically generated FAQ revisions for editorial enhancement. Our findings indicate that LLMs can produce FAQ reformulations beneficial to the editorial process. We observe minimal performance discrepancies among LLMs for this task, and our survey on helpfulness underscores the subjective nature of editors’ perspectives on editorial refinement.
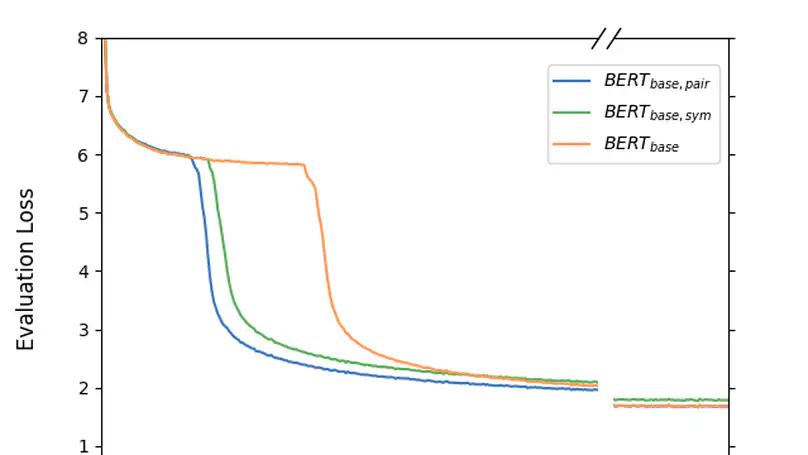
Initially introduced as a machine translation model, the Transformer architecture has now become the foundation for modern deep learning architecture, with applications in a wide range of fields, from computer vision to natural language processing. Nowadays, to tackle increasingly more complex tasks, Transformer-based models are stretched to enormous sizes, requiring increasingly larger training datasets, and unsustainable amount of compute resources. The ubiquitous nature of the Transformer and its core component, the attention mechanism, are thus prime targets for efficiency research.In this work, we propose an alternative compatibility function for the self-attention mechanism introduced by the Transformer architecture. This compatibility function exploits an overlap in the learned representation of the traditional scaled dot-product attention, leading to a symmetric with pairwise coefficient dot-product attention. When applied to the pre-training of BERT-like models, this new symmetric attention mechanism reaches a score of 79.36 on the GLUE benchmark against 78.74 for the traditional implementation, leads to a reduction of 6% in the number of trainable parameters, and reduces the number of training steps required before convergence by half.
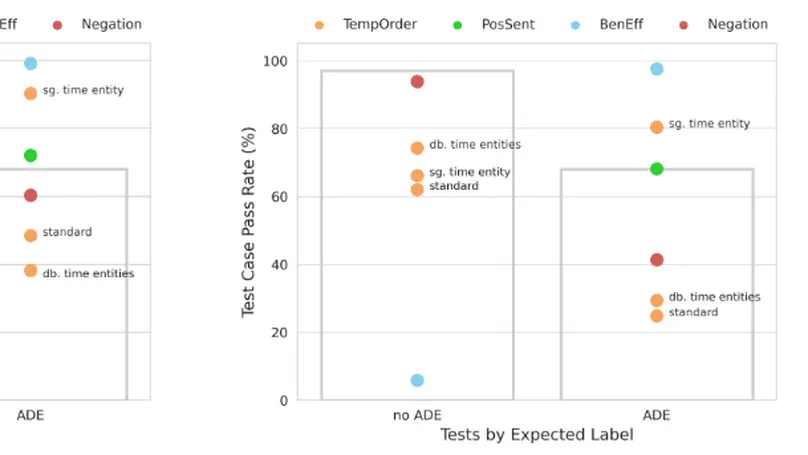
An adverse drug effect (ADE) is any harmful event resulting from medical drug treatment. Despite their importance, ADEs are often under-reported in official channels. Some research has therefore turned to detecting discussions of ADEs in social media. Impressive results have been achieved in various attempts to detect ADEs. In a high-stakes domain such as medicine, however, an in-depth evaluation of a model′s abilities is crucial. We address the issue of thorough performance evaluation in detecting ADEs with hand-crafted templates for four capabilities, temporal order, negation, sentiment and beneficial effect. We find that models with similar performance on held-out test sets have varying results on these capabilities.
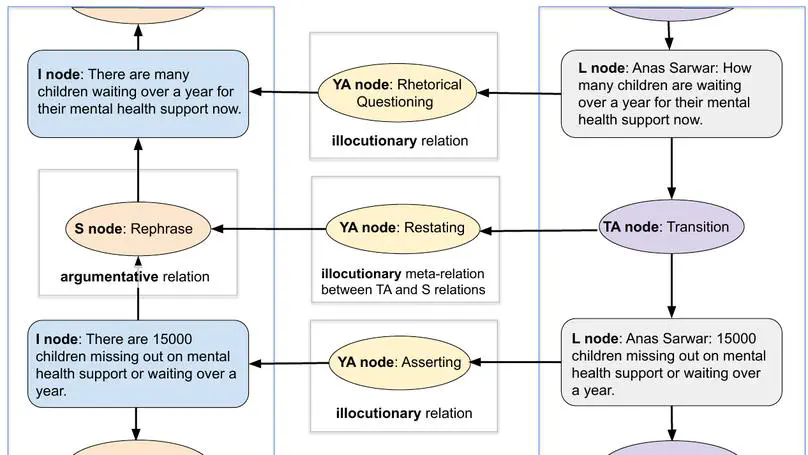
This paper presents the dfki-mlst submission for the DialAM shared task (Ruiz-Dolz et al., 2024) on identification of argumentative and illocutionary relations in dialogue. Our model achieves best results in the global setting: 48.25 F1 at the focused level when looking only at the related arguments/locutions and 67.05 F1 at the general level when evaluating the complete argument maps. We describe our implementation of the data pre-processing, relation encoding and classification, evaluating 11 different base models and performing experiments with, e.g., node text combination and data augmentation. Our source code is publicly available.